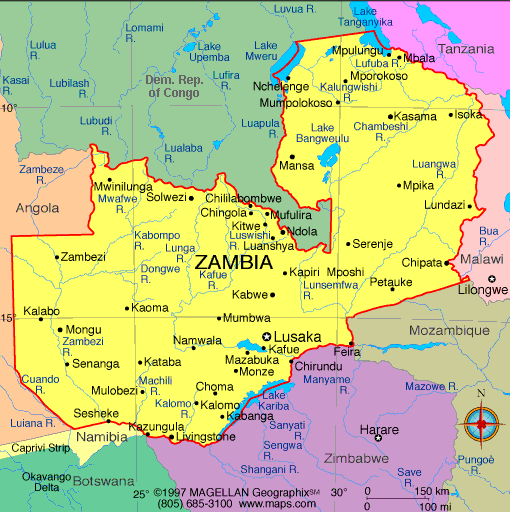
ABOUT ZAMBIA
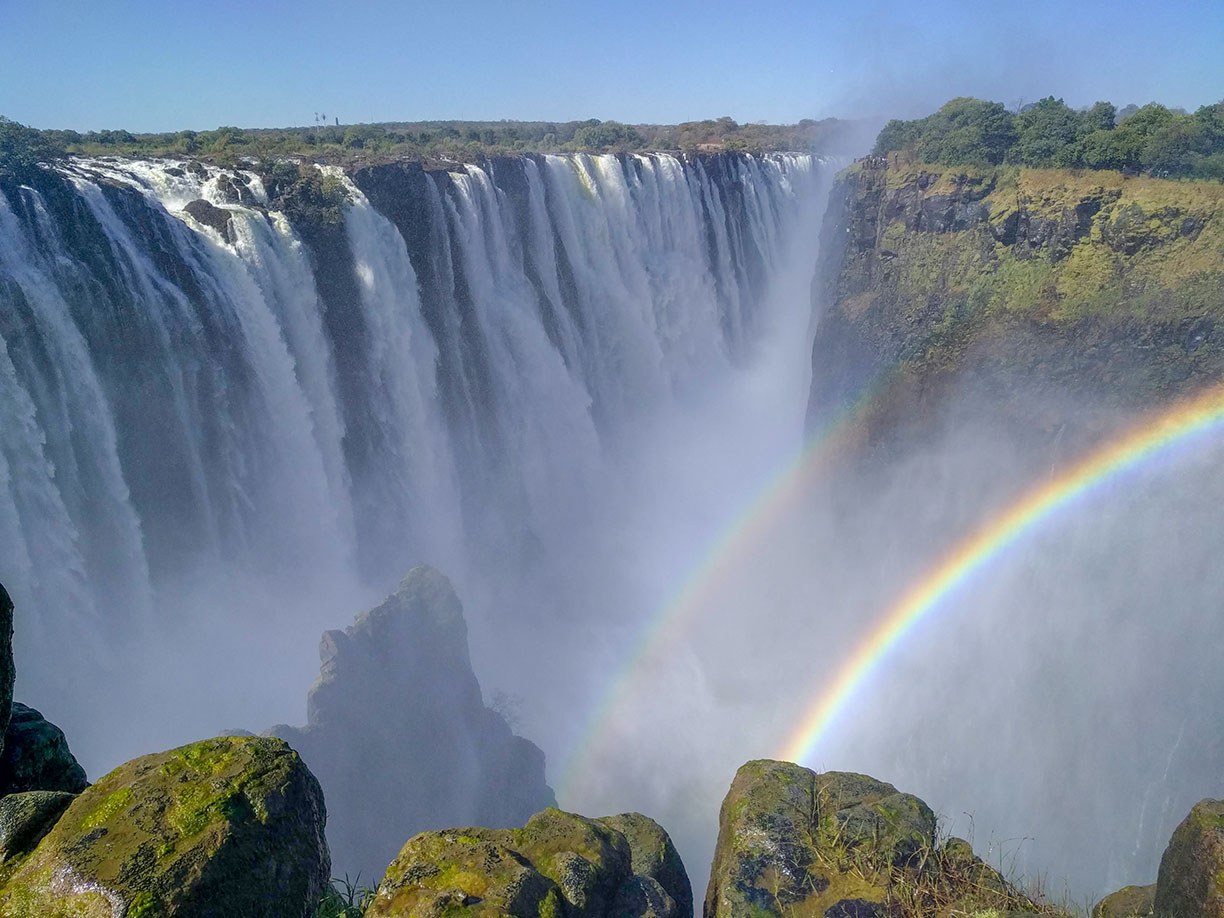
Zambia, in southern Africa, is a landlocked country of rugged terrain and diverse wildlife, with many parks and safari areas. On its border with Zimbabwe is famed Victoria Falls – indigenously called Mosi-oa-Tunya, or “Smoke That Thunders” – plunging a misty 108m into narrow Batoka Gorge. Spanning the Zambezi River just below the falls is Victoria Falls Bridge, a spectacular viewpoint. ― Google
Capital: Lusaka
Population: 18.38 million (2020) World Bank
Currency: Zambian kwacha
Continent: Africa